紧接着上篇文章,这篇文章讲述 Consumer 提供的两种 commit 机制和两种 partition 分配机制,具体如何使用是需要用户结合具体的场景进行选择,本文讲述一下其底层实现。
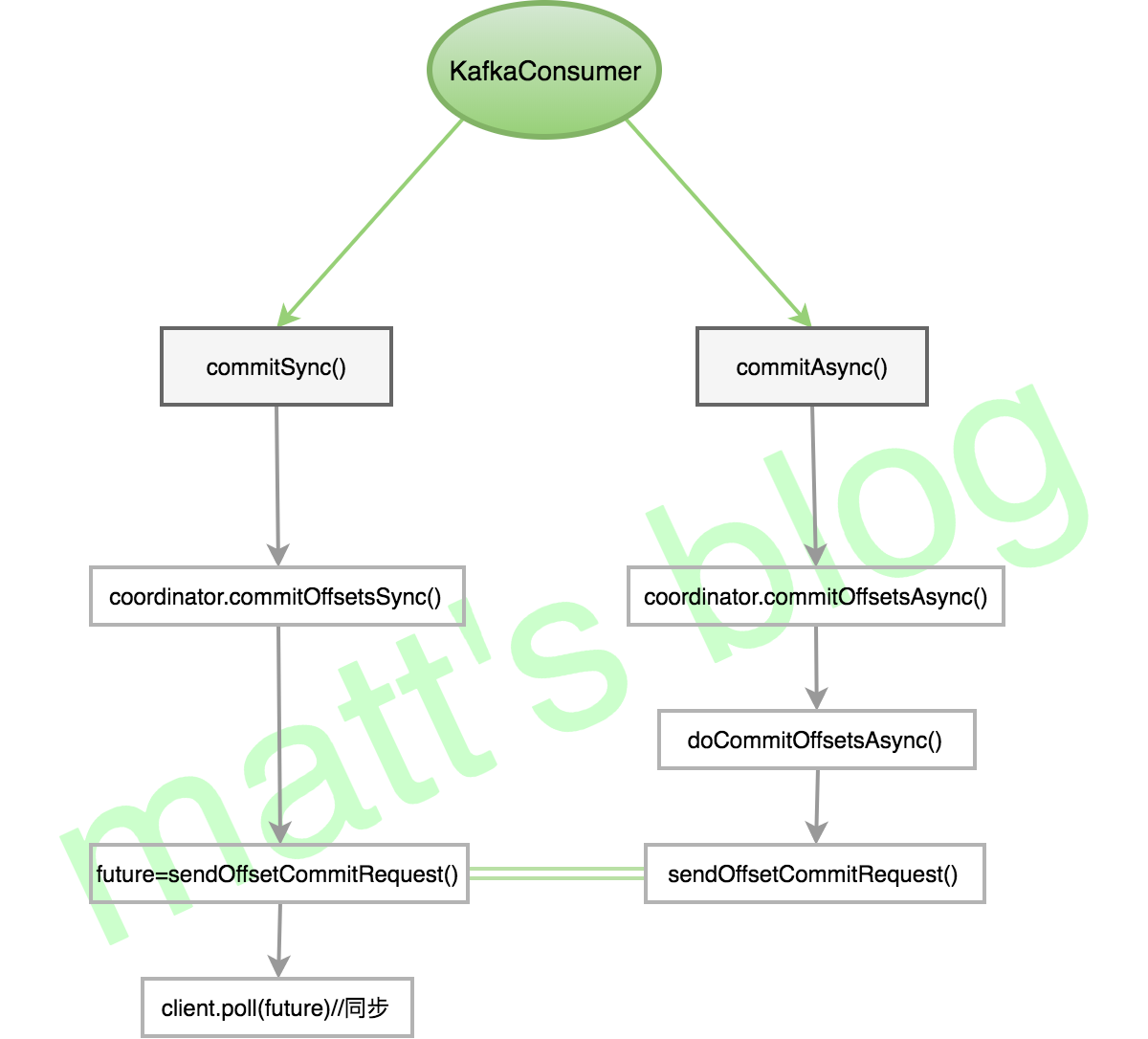
两种 commit 机制 先看下两种不同的 commit 机制,一种是同步 commit,一种是异步 commit,既然其作用都是 offset commit,应该不难猜到它们底层使用接口都是一样的,其调用流程如下图所示:
同步 commit 1 2 3 4 5 6 public void commitSync () public void commitSync (final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets)
其实,从上图中,就已经可以看出,同步 commit 的实现方式,client.poll() 方法会阻塞直到这个request 完成或超时才会返回。
异步 commit 1 2 3 4 public void commitAsync () public void commitAsync (OffsetCommitCallback callback) public void commitAsync (final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, OffsetCommitCallback callback)
而对于异步的 commit,最后调用的都是 doCommitOffsetsAsync 方法,其具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private void doCommitOffsetsAsync (final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, final OffsetCommitCallback callback) this .subscriptions.needRefreshCommits(); RequestFuture<Void> future = sendOffsetCommitRequest(offsets); final OffsetCommitCallback cb = callback == null ? defaultOffsetCommitCallback : callback; future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess (Void value) if (interceptors != null ) interceptors.onCommit(offsets); completedOffsetCommits.add(new OffsetCommitCompletion(cb, offsets, null )); } @Override public void onFailure (RuntimeException e) Exception commitException = e; if (e instanceof RetriableException) commitException = new RetriableCommitFailedException(e); completedOffsetCommits.add(new OffsetCommitCompletion(cb, offsets, commitException)); } }); }
在异步 commit 中,可以添加相应的回调函数,如果 request 处理成功或处理失败,ConsumerCoordinator 会通过 invokeCompletedOffsetCommitCallbacks() 方法唤醒相应的回调函数。
关于 offset commit 请求的处理见上一篇文章中的Offset Commit 请求处理 ,对于提交的 offset,GroupCoordinator 会记录在 GroupMetadata 对象中。
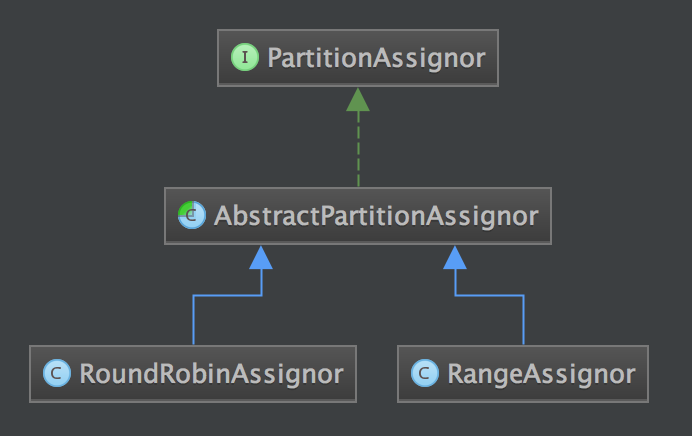
两种 partition 分配机制 consumer 提供的两种不同 partition 分配策略,可以通过 partition.assignment.strategy 参数进行配置,默认情况下使用的是 org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RangeAssignor,Kafka 中提供另一种 partition 的分配策略 org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RoundRobinAssignor,它们关系如下图所示:
通过上图可以看出,用户可以自定义相应的 partition 分配机制,只需要继承这个 AbstractPartitionAssignor 抽象类即可。
AbstractPartitionAssignor AbstractPartitionAssignor 有一个抽象方法,如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public abstract Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions);
assign() 这个方法,有两个参数:
partitionsPerTopic:所订阅的每个 topic 与其 partition 数的对应关系,metadata 没有的 topic 将会被移除;subscriptions:每个 consumerId 与其所订阅的 topic 列表的关系。
RangeAssignor 和 RoundRobinAssignor 通过这个方法 assign() 的实现,来进行相应的 partition 分配。
RangeAssignor 分配模式 直接看一下这个方法的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic, Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) { Map<String, List<String>> consumersPerTopic = consumersPerTopic(subscriptions); Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>(); for (String memberId : subscriptions.keySet()) assignment.put(memberId, new ArrayList<TopicPartition>()); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> topicEntry : consumersPerTopic.entrySet()) { String topic = topicEntry.getKey(); List<String> consumersForTopic = topicEntry.getValue(); Integer numPartitionsForTopic = partitionsPerTopic.get(topic); if (numPartitionsForTopic == null ) continue ; Collections.sort(consumersForTopic); int numPartitionsPerConsumer = numPartitionsForTopic / consumersForTopic.size(); int consumersWithExtraPartition = numPartitionsForTopic % consumersForTopic.size(); List<TopicPartition> partitions = AbstractPartitionAssignor.partitions(topic, numPartitionsForTopic); for (int i = 0 , n = consumersForTopic.size(); i < n; i++) { int start = numPartitionsPerConsumer * i + Math.min(i, consumersWithExtraPartition); int length = numPartitionsPerConsumer + (i + 1 > consumersWithExtraPartition ? 0 : 1 ); assignment.get(consumersForTopic.get(i)).addAll(partitions.subList(start, start + length)); } } return assignment; }
假设 topic 的 partition 数为 numPartitionsForTopic,group 中订阅这个 topic 的 member 数为 consumersForTopic.size(),首先需要算出两个值:
numPartitionsPerConsumer = numPartitionsForTopic / consumersForTopic.size():表示平均每个 consumer 会分配到几个 partition; consumersWithExtraPartition = numPartitionsForTopic % consumersForTopic.size():表示平均分配后还剩下多少个 partition 未分配。
分配的规则是:对于剩下的那些 partition 分配到前 consumersWithExtraPartition 个 consumer 上,也就是前 consumersWithExtraPartition 个 consumer 获得 topic-partition 列表会比后面多一个。
在上述的程序中,举了一个例子,假设有一个 topic 有 7 个 partition,group 有5个 consumer,这个5个 consumer 都订阅这个 topic,那么 range 的分配方式如下:
consumer 0:start: 0, length: 2, topic-partition: p0,p1;
consumer 1:start: 2, length: 2, topic-partition: p2,p3;
consumer 2:start: 4, length: 1, topic-partition: p4;
consumer 3:start: 5, length: 1, topic-partition: p5;
consumer 4:start: 6, length: 1, topic-partition: p6
而如果 group 中有 consumer 没有订阅这个 topic,那么这个 consumer 将不会参与分配。下面再举个例子,将有两个 topic,一个 partition 有5个,一个 partition 有7个,group 有5个 consumer,但是只有前3个订阅第一个 topic,而另一个 topic 是所有 consumer 都订阅了,那么其分配结果如下:
consumer
订阅的 topic1 的列表
订阅的 topic2 的列表
consumer 0
t1p0, t1p1
t2p0, t2p1
consumer 1
t1p2, t1p3
t2p2, t2p3
consumer 2
t1p4
t2p4
consumer 3
t2p5
consumer 4
t2p6
RoundRobinAssignor 这个是 roundrobin 的实现,其实现方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Override public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic, Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) { Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>(); for (String memberId : subscriptions.keySet()) assignment.put(memberId, new ArrayList<TopicPartition>()); CircularIterator<String> assigner = new CircularIterator<>(Utils.sorted(subscriptions.keySet())); for (TopicPartition partition : allPartitionsSorted(partitionsPerTopic, subscriptions)) { final String topic = partition.topic(); while (!subscriptions.get(assigner.peek()).contains(topic)) assigner.next(); assignment.get(assigner.next()).add(partition); } return assignment; } public List<TopicPartition> allPartitionsSorted (Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic, Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) SortedSet<String> topics = new TreeSet<>(); for (List<String> subscription : subscriptions.values()) topics.addAll(subscription); List<TopicPartition> allPartitions = new ArrayList<>(); for (String topic : topics) { Integer numPartitionsForTopic = partitionsPerTopic.get(topic); if (numPartitionsForTopic != null ) allPartitions.addAll(AbstractPartitionAssignor.partitions(topic, numPartitionsForTopic)); } return allPartitions; }
roundrobin 的实现原则,简单来说就是:列出所有 topic-partition 和列出所有的 consumer member,然后开始分配,一轮之后继续下一轮,假设有有一个 topic,它有7个 partition,group 有3个 consumer 都订阅了这个 topic,那么其分配方式为:
consumer
分配列表
consumer 0
tp0, tp3, tp6
consumer 1
tp1, tp4
consumer 2
tp2, tp5
对于多个 topic 的订阅,将有两个 topic,一个 partition 有5个,一个 partition 有7个,group 有5个 consumer,但是只有前3个订阅第一个 topic,而另一个 topic 是所有 consumer 都订阅了,那么其分配结果如下:
consumer
订阅的 topic1 的列表
订阅的 topic2 的列表
consumer 0
t1p0, t1p3
t2p0, t2p5
consumer 1
t1p1, t1p4
t2p1, t2p6
consumer 2
t1p2
t2p2
consumer 3
t2p3
consumer 4
t2p4
roundrobin 分配方式与 range 的分配方式还是略有不同。